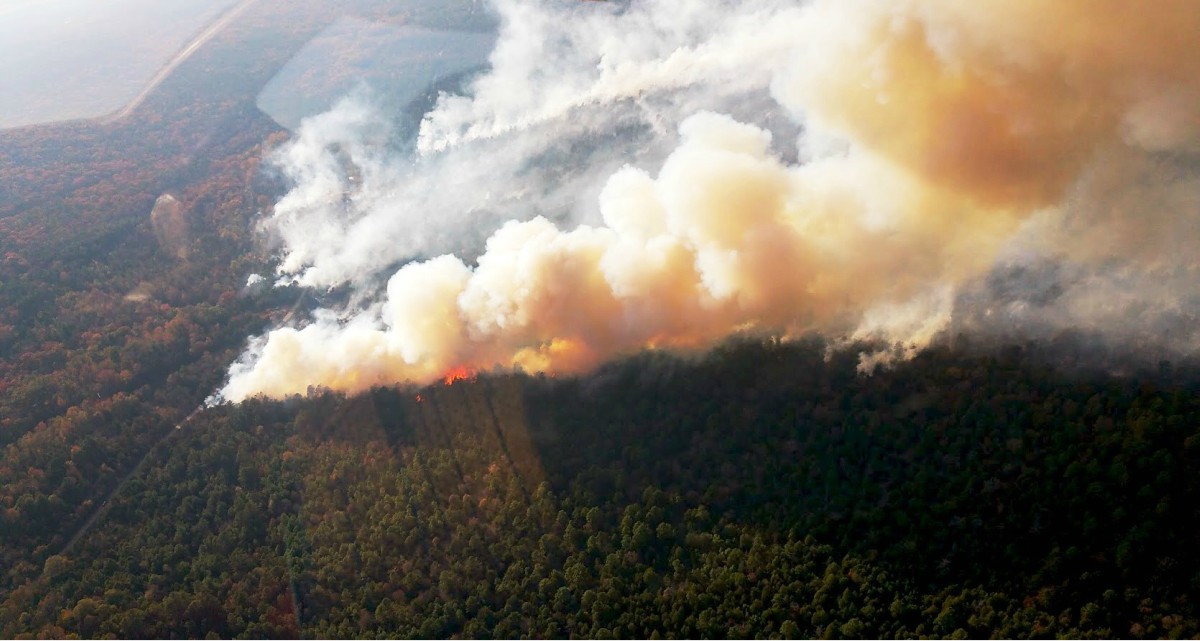
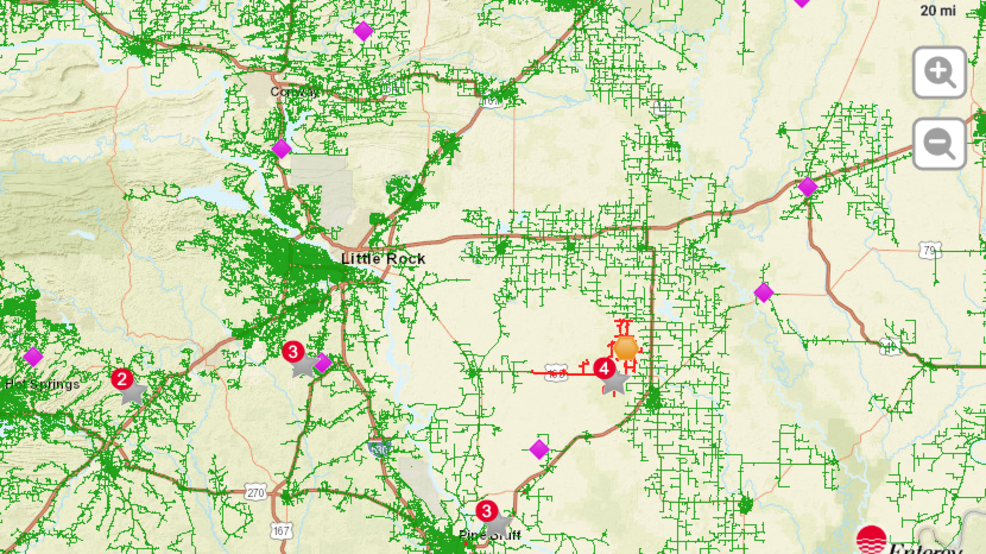
Wildfires and power outages across Arkansas have become increasingly alarming issues in recent years. The state's unique geographical and climatic conditions make it particularly vulnerable to such disasters, affecting not only the environment but also the lives of its residents. As the frequency and intensity of wildfires rise, so does the risk of widespread power outages, leaving communities grappling with significant disruptions.
Arkansas, known for its lush forests and diverse landscapes, is now facing unprecedented challenges due to these natural disasters. The impact of wildfires on infrastructure, air quality, and public health cannot be overstated. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the causes, effects, and potential solutions to wildfires and power outages in Arkansas, ensuring that residents and stakeholders are well-informed and prepared.
By understanding the root causes and adopting effective strategies, we can mitigate the risks associated with wildfires and power outages across Arkansas. This knowledge is crucial not only for policymakers and emergency responders but also for everyday citizens who must navigate these challenges in their daily lives.
Read also:Lawrence Wong Actor
Table of Contents
- Causes of Wildfires in Arkansas
- Impact of Wildfires on Power Outages
- Biological and Environmental Factors
- Infrastructure Vulnerabilities
- Solutions and Preventive Measures
- Community Preparedness
- Government Initiatives
- Key Statistics and Data
- Future Outlook and Challenges
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Causes of Wildfires in Arkansas
Wildfires in Arkansas are primarily caused by a combination of natural and human factors. Lightning strikes, dry weather conditions, and high winds contribute significantly to the ignition and spread of fires. However, human activities such as unattended campfires, arson, and improper disposal of cigarettes also play a critical role in exacerbating the problem.
Climate Change and Its Role
Climate change has intensified the frequency and severity of wildfires in Arkansas. Rising temperatures and prolonged droughts create ideal conditions for fires to ignite and spread rapidly. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the state has experienced a noticeable increase in extreme weather events over the past decade, directly impacting wildfire patterns.
Vegetation and Fuel Load
Arkansas' dense forests and abundant vegetation serve as fuel for wildfires. Dead trees, dry leaves, and other organic materials accumulate over time, creating a tinderbox effect during dry spells. Effective forest management practices are essential to reduce the fuel load and minimize fire risks.
Impact of Wildfires on Power Outages
Wildfires often lead to widespread power outages across Arkansas, disrupting essential services and daily life for residents. The destruction of power lines, substations, and other critical infrastructure exacerbates the situation, leaving communities without electricity for extended periods.
Economic Consequences
The economic impact of wildfires and power outages is substantial. Businesses suffer from lost productivity, and households face increased expenses due to damaged property and emergency repairs. According to a report by the Arkansas Department of Emergency Management, the state incurs millions of dollars in damages annually due to these disasters.
Public Health Risks
Air pollution caused by wildfires poses significant health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and individuals with respiratory conditions. The fine particulate matter released during fires can penetrate deep into the lungs, leading to respiratory issues and other health complications.
Read also:Taron Egertons Brother A Comprehensive Look Into His Life And Influence
Biological and Environmental Factors
The ecological balance of Arkansas is severely disrupted by wildfires. Native wildlife habitats are destroyed, leading to a decline in biodiversity. Soil erosion and water contamination are additional environmental concerns that arise from these disasters.
Restoration Efforts
- Reforestation projects to restore damaged ecosystems
- Collaboration with environmental organizations to promote conservation
- Education programs to raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity
Infrastructure Vulnerabilities
Arkansas' power grid infrastructure is particularly vulnerable to wildfires. Aging equipment and inadequate maintenance contribute to the risk of power outages during fire events. Upgrading and modernizing the grid is essential to enhance resilience and reliability.
Investment in Smart Grid Technology
Implementing smart grid technology can significantly improve the ability to detect and respond to power outages caused by wildfires. Real-time monitoring and automated systems enable faster restoration of power, reducing the impact on affected communities.
Solutions and Preventive Measures
Addressing the challenges of wildfires and power outages in Arkansas requires a multi-faceted approach. Combining advanced technology, community engagement, and policy reforms can lead to effective solutions.
Fire Prevention Strategies
- Regular forest thinning and controlled burns to reduce fuel load
- Public education campaigns to promote safe fire practices
- Installation of fire detection systems in high-risk areas
Community Preparedness
Empowering communities to prepare for wildfires and power outages is crucial for minimizing their impact. Residents should have access to resources and information to ensure their safety during emergencies.
Emergency Preparedness Kits
- First aid supplies
- Non-perishable food and water
- Flashlights and batteries
Government Initiatives
The Arkansas state government has implemented several initiatives to address the challenges of wildfires and power outages. These efforts focus on enhancing emergency response capabilities, improving infrastructure, and promoting sustainable practices.
Collaboration with Federal Agencies
Partnering with federal agencies such as the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) and the U.S. Forest Service ensures that Arkansas has access to the necessary resources and expertise to tackle these issues effectively.
Key Statistics and Data
Data and statistics provide valuable insights into the scope and impact of wildfires and power outages in Arkansas. According to the Arkansas Forestry Commission, the state experienced over 1,000 wildfires in 2022, resulting in the destruction of thousands of acres of land.
Historical Trends
Examining historical data reveals a clear trend of increasing wildfire occurrences and severity. This information underscores the urgency of implementing comprehensive strategies to address these challenges.
Future Outlook and Challenges
Looking ahead, Arkansas faces significant challenges in managing wildfires and power outages. The continued effects of climate change, population growth, and urban expansion will likely exacerbate these issues. However, with proactive measures and collaboration, the state can work towards a safer and more resilient future.
Innovative Technologies
Emerging technologies such as drone surveillance, artificial intelligence, and renewable energy solutions offer promising opportunities to mitigate the risks associated with wildfires and power outages. Investing in research and development in these areas can yield long-term benefits for Arkansas.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Wildfires and power outages across Arkansas pose significant challenges that require immediate attention and action. By understanding the causes, impacts, and solutions, we can work together to protect our communities and environment. Residents are encouraged to stay informed, prepare for emergencies, and advocate for policies that prioritize sustainability and resilience.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our website to learn more about environmental issues and solutions. Together, we can make a difference in creating a safer and more sustainable Arkansas for future generations.